Introduction
This project describes the design and implementation of a robot that uses the STM32F303 Discovery board to control hardware and a Python server application with OpenAI GPT API to process audio signals and generate commands. The main goal of the project is to create an autonomous system that can process audio commands using artificial intelligence and convert them into appropriate signals for motor control.
This system enables integration of embedded systems with modern natural language processing, using a server application for communication between user commands and the robot's motor control. The robot represents a practical application of combining low-level embedded programming with high-level AI-powered speech recognition, demonstrating how modern technologies can work together to create intelligent robotic systems.
System Overview
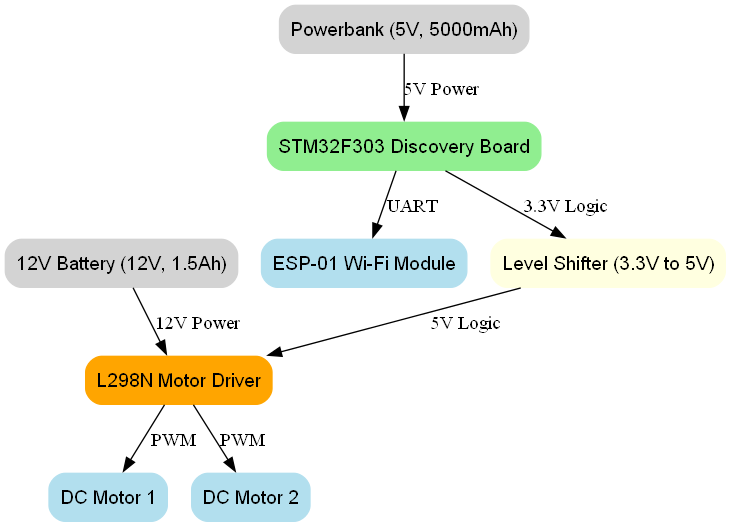
The robot consists of several key components that together provide complete functionality. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall system architecture, from power delivery to motor control to wireless communication. The integration of these components required careful consideration of voltage levels, communication protocols, and mechanical design.
Core Components:
STM32F303 Discovery Board serves as the main system controller. This development board is based on the STM32F303VCT6 microcontroller which features a 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4 processor. The board is ideal for developing embedded systems due to its rich peripheral equipment and support for various communication protocols. It provides 256 KB of Flash memory and 48 KB of SRAM, which is more than sufficient for the control algorithms and communication handling required by this project. The board also includes a built-in ST-LINK/V2 for debugging and programming, making development and troubleshooting significantly easier.
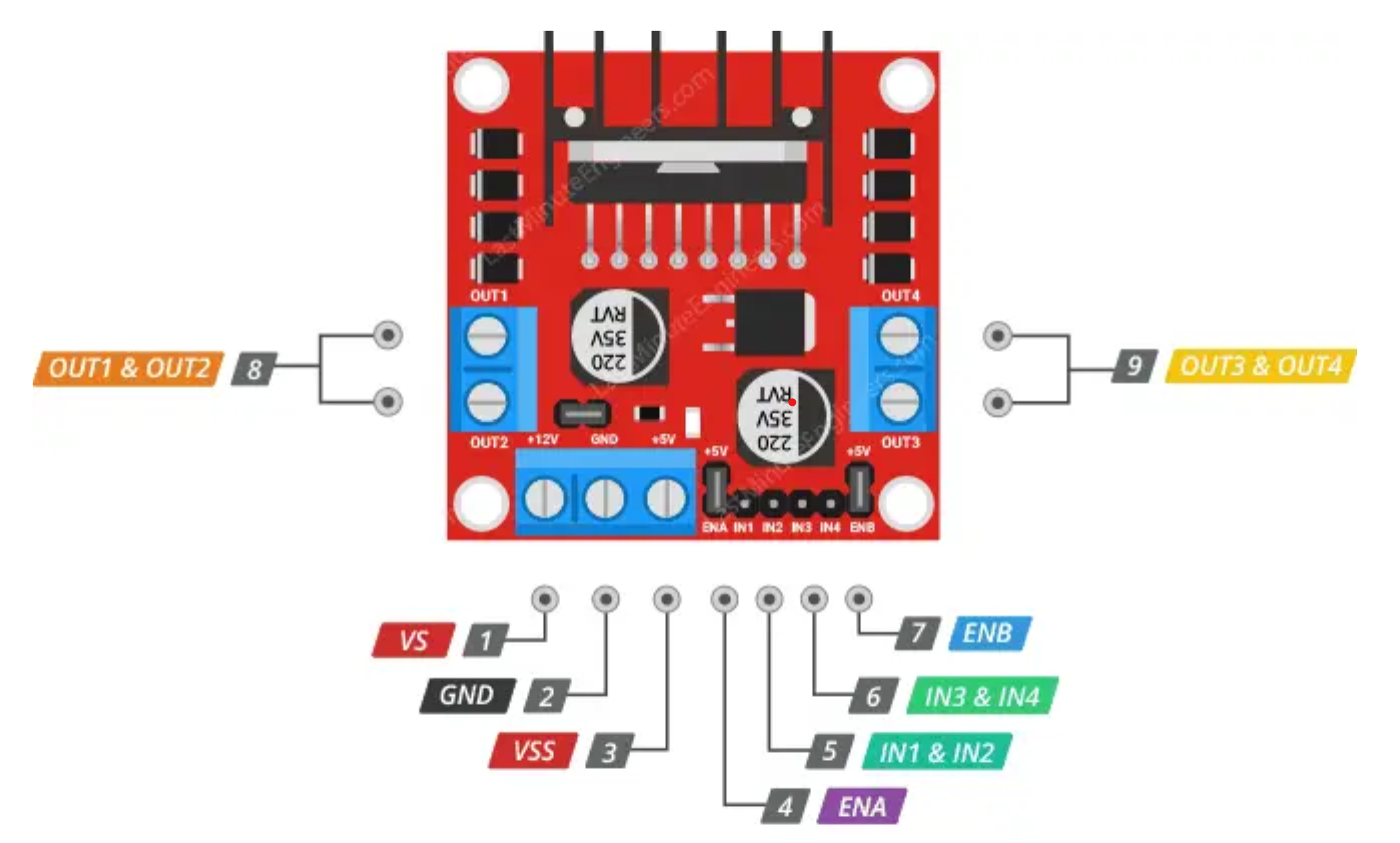
L298N Motor Driver is a dual-channel H-bridge motor driver that enables independent control of two DC motors. This component is essential for controlling the robot's movement, as it can handle voltages up to 46V and currents up to 2A per channel, making it suitable for various applications. The driver receives PWM signals for speed control and digital signals for direction control from the STM32, translating these into the high-current signals needed to drive the motors.
12V DC Brushed Motors with 50:1 Metal Gearbox are used for the rear wheels. The robot uses two of these motors, which are ideal for applications requiring high torque and precise movement at low speeds. The 50:1 gear ratio means that for every 50 rotations of the motor shaft, the output shaft rotates once, providing significant torque multiplication. This high torque is essential for moving the robot's weight and overcoming friction, especially when starting from a standstill or climbing slight inclines.
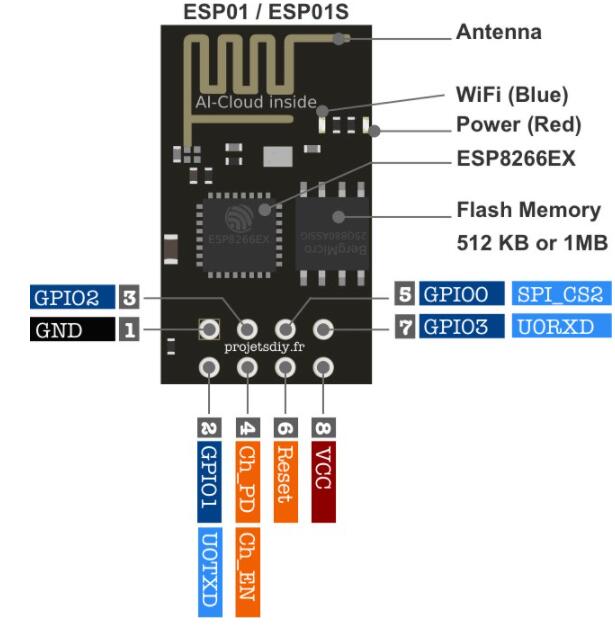
ESP-01 Wi-Fi Module is a compact Wi-Fi module based on the ESP8266 chip. It enables wireless communication via Wi-Fi networks and is ideal for IoT applications. The module communicates with the STM32 via UART interface and can operate as either a station (connecting to existing Wi-Fi) or as an Access Point. In this project, it operates in station mode, connecting to a local Wi-Fi network to communicate with the Python server.
Bidirectional Logic Level Converter is necessary because the L298N driver operates on 5V logic while the PWM generator from the STM32F303 operates on 3.3V. This converter ensures safe voltage level matching and protects components from potential damage due to voltage mismatch. It's important to note that all elements should be connected to a common ground (GND) for better protection and signal integrity.
Power System consists of two separate power sources to meet the different requirements of the system. A 12V drill battery (1.5 Ah, 16.64 Wh) powers the motor driver and motors, providing the high current needed for motor operation. A 5V Powerbank (5000 mAh, 2.1A) powers the STM32 microcontroller and logic components, ensuring clean, stable power for the sensitive digital electronics.
Mechanical Construction
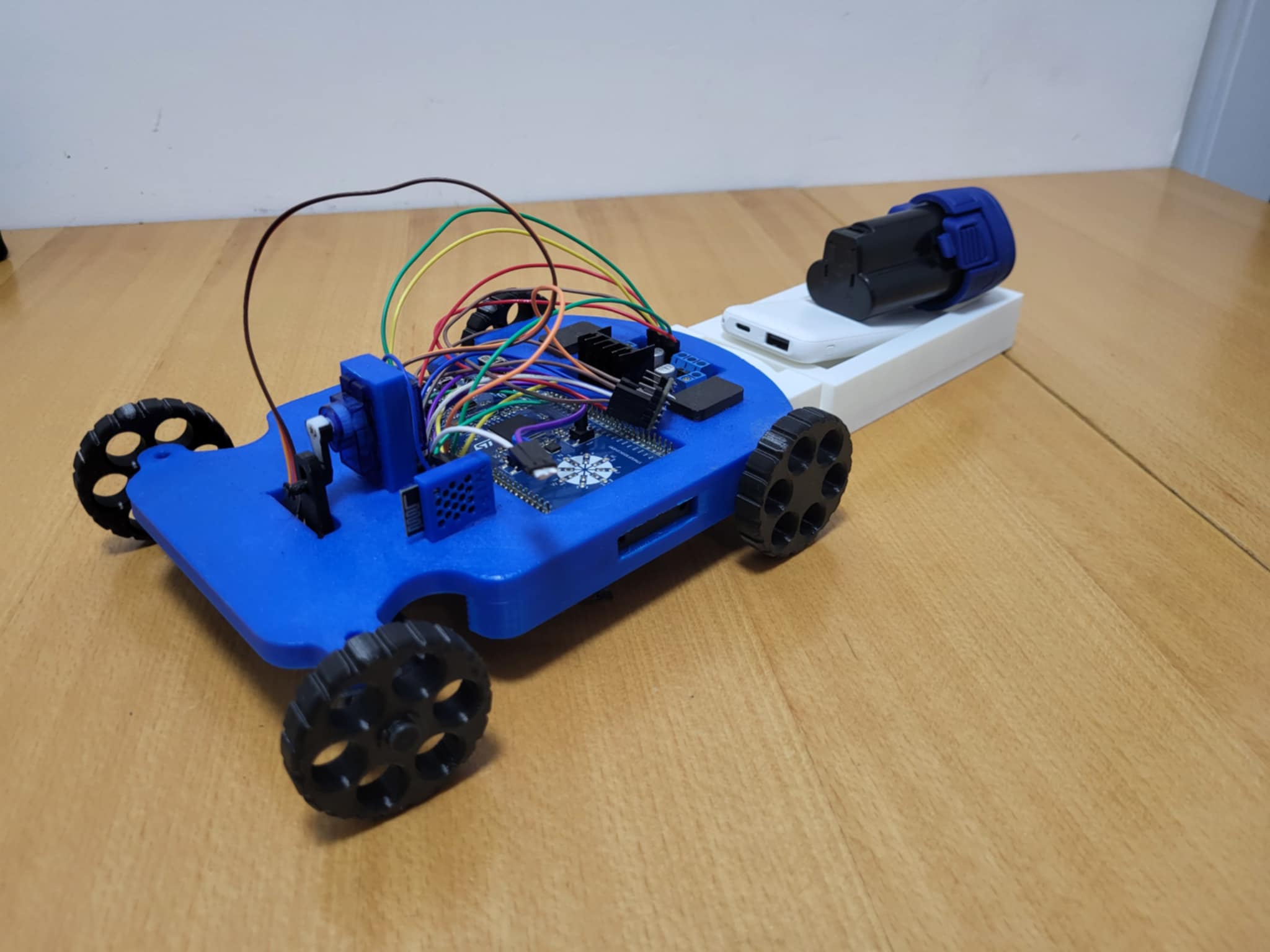
The robot chassis is 3D printed and designed as a cart-style platform. This construction allows easy mounting of components and provides stability during movement. The cart design was chosen for its simplicity and effectiveness - it provides a large, flat surface for mounting electronics while maintaining a low center of gravity for stability.
The chassis consists of several 3D printed parts, all designed to work together as a cohesive mechanical system. The main chassis base serves as the foundation, with mounting points for motors, electronics, and wheels carefully positioned to ensure proper weight distribution and mechanical advantage.